Financial statements work like the financial dashboard that informs the incomings and outgoings of a business. If you lack these statements, you might be unable to plan your expenses, get loans and sell your business. But how to create these statements? The answer is Accounting Cycle.
It is a key component to perform bookkeeping tasks accurately and for healthy financial management. This cycle is also called the bookkeeping cycle. It is aimed to turn your raw financial information into financial statements and helps you to make better business decisions.
Accotax is a dedicated accountancy firm based in Morden, UK. Call us at 020 3441 1258 or send us an email at [email protected].
Accounting Cycle
It is a thorough process of recording, processing and summarising/reporting the financial activities of a business. This process starts after the first business transaction and ends with closing entries on financial statements. A bookkeeper holds the responsibility to manage it from the start to the end.
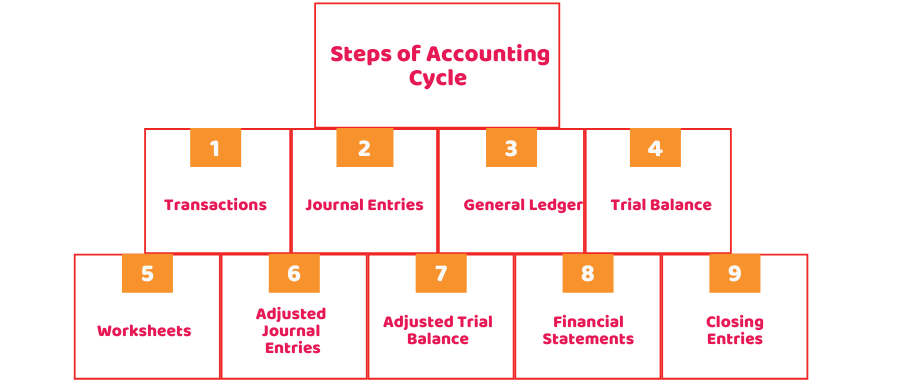
Steps of Accounting Cycle
There are different steps involved in this cycle. These steps can vary based on the bookkeeper or accountant you are working with. To put it simply, here are the most common steps:
1) Transactions
The first and basic step of this cycle is identifying and recording transactions. Without these, you can’t keep track of anything in this cycle. Transitions include receipts, bank statements, invoices and other things like sales, expenses, payments in an accounting year.
A business will have numerous transactions in an accounting period. These transactions would trigger the beginning of this cycle.
2) Journal Entries
The second step is to post the transactions into the company’s accounting journal. You need to record these entries in a chronological sequence. Bookkeepers post these entries by using double-entry bookkeeping. Here, when one account is debited, the other must be credited. Remember that both debit and credit entries need to be in balance.
3) General Ledger
After recording transactions as journal entries, they need to be posted in the account of the general ledger. The general ledger divides all the accounting activities into different accounts. It eases the job of the bookkeeper to manage and monitor financial positions and the status of transactions by assigning each transaction different accounts.
Have a query? Why not speak to one of our experts and see how we can help you are looking for!
4) Trial Balance
The next step is to prepare an unadjusted trial balance. At the end of every accounting year, the overall balance of every single general ledger needs to be calculated. A company’s accounting period can be monthly, quarterly or annual.
Moreover, the trial balance verifies that the total debits are equal to the total credits. At this stage, accuracy doesn’t need to be checked, as wrong balances would be evident.
5) Worksheets
The fifth step is to analyse the worksheet and make corrections. If there is any mistake in the trial balance and both sides (credit and debt) don’t match, the bookkeeper needs to find out the error and do the required adjustments that are tracked on a worksheet.
In addition to making corrections, adjusting entries may also be used for matching revenue and expense in accrual accounting.
6) Adjusted Journal Entries
Although they are recorded in chronological order, you need to ensure that expenses and revenues are assigned to the right accounting period. A bookkeeper makes adjustments and records as journal entries where necessary.
7) Adjusted Trial Balance
After posting adjusting journal entries, now you are required to adjust the trial balance too. It has the same purpose as the first trial balance. So once again, you need to verify that there is no discrepancy in credits and debits balances after adjusting entries previously.
8) Financial Statements
After taking the correct figures from the adjusted trial balance, statements of the balance sheet, income and cash flow are made.
9) Closing Entries
The last thing to do after preparing the financial statements is to take the value of revenue and expense accounts to zero to close the process. You’ll carry over zero balance to the start of the next accounting cycle.
Why Use Accounting Cycle for Your Finance?
No matter whether you’re a small business or employ cash accounting methods, this cycle can prove to be beneficial for you in many ways. It ensures the accuracy of our balances by letting you know that you haven’t skipped something during the process. It depicts the real financial health of your business.
Furthermore, this cycle helps you to categorise and adjust the transaction in proper order. In addition, it also ensures that you and your accountant have got a thorough and accurate overview of the financial stability of your business. If you’re using accrual accounting, you must utilise this cycle for the optimal advantage.
Quick Sum Up
The accounting cycle can prove to be a bit difficult for those business owners who lack accounting or bookkeeping background. Therefore, we recommend you hire an expert accountant to do everything for you. By investing in the services of a professional, you can better use your time, energy and resources on other areas of your business.
Count on our bookkeeper and accountants to deal with each stage of your cycle with accuracy. Give us a call on 0203 4411 258 or request a callback. We are available from 9:00 am – 05:30 pm Monday to Friday.
Accotax offers accounting and bookkeeping for SMEs and self-employed individuals in the UK. If you ever need these services turn to Accotax.
Contact us today to get started!
Disclaimer: This article intends to provide general information on the above topic.