In case you are associated with accounting and you have the responsibility of balance sheet for a company. Then classified balance sheet is also a part of your job. Here is a basic guide for beginners that will tell you everything you need to know about how classified balance sheets make accounting easier for you. This will surely keep your accounts more organised and will save you time and effort.
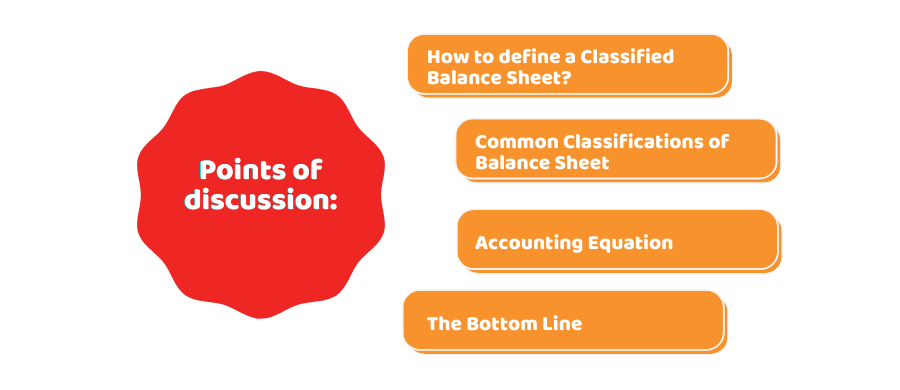
In this article, we will further cover the following points of discussion:
- How to define a Classified Balance Sheet?
- Common Classifications of Balance Sheet
- Accounting Equation
- The Bottom Line
Interested in ACCOTAX – Accountants in London? Why not speak to one of our qualified accountants? Give us a call on 02034411258 or request a callback. We are available from 9:00 am – 05:30 pm Monday to Friday.
How to Define a Classified Balance Sheet?
A financial statement that has classifications that include liabilities, current assets, and other relevant factors is known as a classified balance sheet. With the organised and classified information in accounting, it is a lot easier for accountants to extract any information that is required.
In the comparison of regular balance sheets where details are listed in a long line, it takes a lot of effort and time to find out the information.
Common Classifications of Balance Sheet:
Moreover, it is also possible to look into a company’s business operations, investors and creditors details in this way. Categorising the balance sheet makes it possible to accomplish in a lot more easy way. The most popular and common classifications of the balance sheet are listed below:
- Shareholder Equity
- Long term liabilities
- Current liabilities
- Intangible Assets
- Fixed assets like plant, equipment and property
The details of the above-mentioned classifications are further discussed as:
Shareholder Equity:
It mostly depends on the way a business is being organised. This majorly includes that if it is a sole trader business to carry out, a partnership or a corporation. This part of the balance sheet commonly consists of the following:
- Additional paid capital
- capital stock
- retained earnings
Long Term Liabilities:
These obligations are non-current (that need to be paid over one year). In some cases, this classification can be partially long term liability and partially current. The long term liabilities include:
- Bank and other loans payable
- Deferred tax liabilities
- Mortgage notes
- Other non-current liabilities
Current Liabilities:
Liabilities that are to be liquidated within the time limit of twelve months. Also, they are paid with the use of current assets. Mostly the following listed points are included in this:
- financial liabilities
- current tax liabilities
- accrued expenses
- liabilities for sale
- trade and other payables
- current portion of loans
Intangible Assets:
As the name shows that intangible assets are the ones that include the list of such assets that have no physical existence.
- Franchise agreement and rights
- copyrights
- purchased patents
Get an instant quote based on your requirements online in under 2 minutes, Sign up online or request a callback.
Accounting Equation:
The purpose of the equation is to tell the relationship that is between the liabilities, equity and assets of your company. Commonly accounting equation is also known as the balance sheet equation. It is important that the total of the classification matches the accounting equation on the classified balance sheet. The equation is mentioned below:
total liabilities + shareholders’ equity = total assets
Both sides of the equation must be equal. This makes it easier to understand how your company is doing financially and the relationship between your financial statements.
Looking for all-inclusive monthly packages? Let us take care of your affairs so that you can focus on your business.
The Bottom Line:
Now that you know what is classified balance sheet, we can sum up the discussion by saying that it makes the accounting process a lot easier and manageable. The process becomes less time-consuming and saves your energies to invest in a more productive way to increase your business valuation.
However, to enjoy the benefits it is important to follow the professional method and make seamless accounting possible and advanced. We hope this article helped to develop a better understanding.
Can’t find what you are looking for? why not speak to one of our experts and see how we can help you are looking for.
Disclaimer: This article intends to provide general information based on the classified balance sheet.