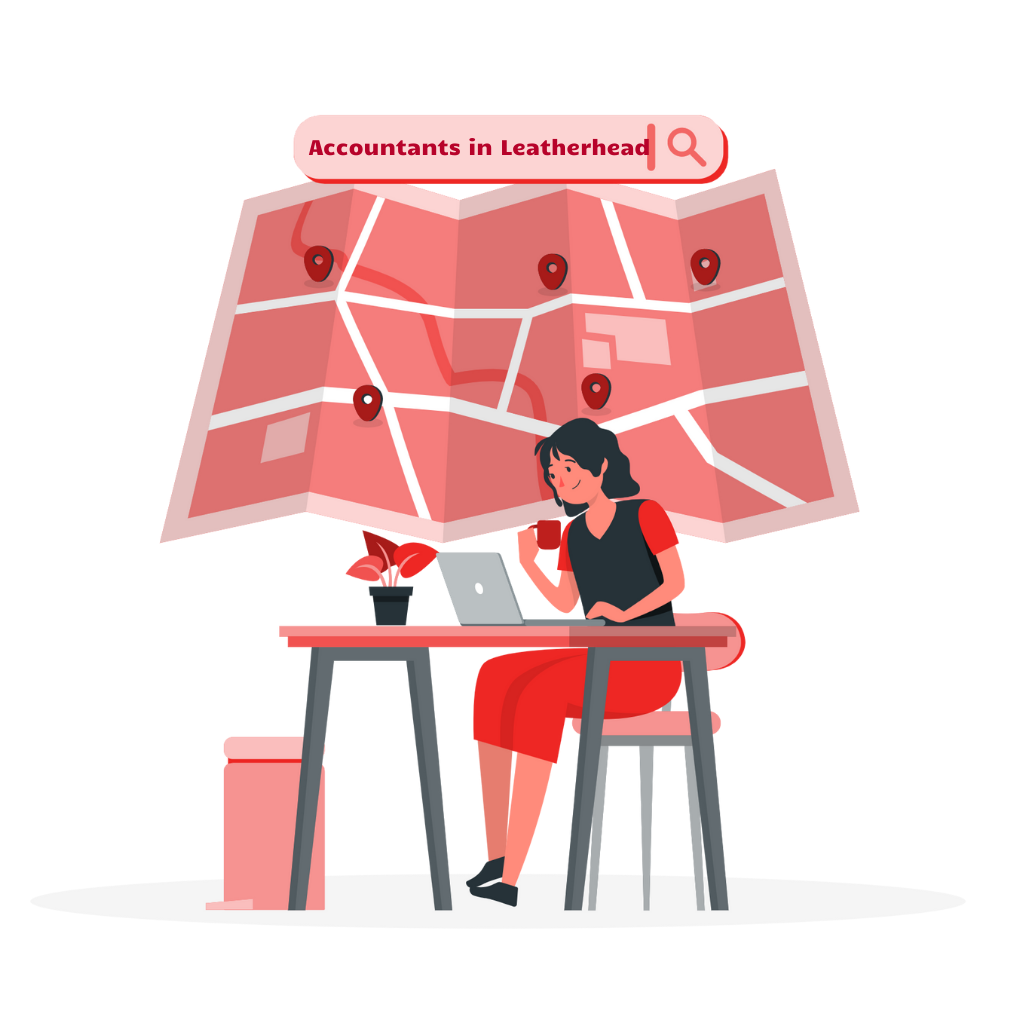
There is still plenty of uncertainty about potential cuts in pension tax benefits as things stand at present. Paying into a pension generally remains a tax-efficient way of saving for old-age. Given that there may well be future changes in this area. It might be beneficial to consider starting. Thus, or topping up pension plans sooner rather than later.
Most employer pension contributions will count as allowable business expenses. So a company could currently save up to 19% in corporation tax if it makes qualifying contributions on behalf of its employees. This may be particularly beneficial in a family-owned company. Where pensions for family members can built up whist saving. Thus, both the investor and the company money. To qualify for a deduction. The pension contributions should be ‘wholly and only’ for the purposes of business. HMRC will check for evidence that this is the case. For example, whether other employees are receiving comparable Payment packages.
Reliefs
Subject to certain conditions, tax relief is currently available on pension contributions. Which at the highest rate of income tax paid meaning that basic rate taxpayers get relief on contributions at 20%. At higher rate taxpayers at 40%, and extra rate taxpayers at 45%. In Scotland, income tax is band, and pension tax relief applies in a different way.
A contribution of £100, will currently only cost a basic rate taxpayer £80. The contribution deems as made by a net of tax (£80). Thus, the pension provider claims tax relief (£20) from the government. The gross contribution (£100) is invested in the pension plan. Higher rate and extra rate taxpayers need only to pay £60 and £55 to achieve the same £100 of pension savings.
Pensions are a particularly tax-efficient form of savings since everyone is entitled. Thus, to receive relief on contributions up to an annual max regardless of whether they pay tax or not. The max amount on which a non-taxpayer can currently receive basic rate tax relief is £3,600. So, an individual can pay in £2,880 a year, but £3,600 will be the amount actually invested by the pension provider. Higher amounts may be invested, but tax relief will not give on the excess. Any tax relief received from HMRC on excess contributions may have to be repaid.
It’s worth noting that where family members employed. The pension contributions paid by the company there needs to be a genuine business reason for it. The family member should pay a commercial amount for work. That they have actually undertaken, and the company should be able to prove that this is the case.
Auto-enrolment
A spouse/civil partner or another family member may employed to help with a business. If they are pay a salary and they are not a director. They may be an ‘eligible worker’. Which means the business may need to enrol them into a pension scheme. A worker that is eligible to join a workplace pension is an employee aged between 22. Thus, the state pension age that is pay over £833 per month or £192 per week.
If they are a director, there may still be enrolment obligations. See Pensions Advisory service at www.pensionsadvisoryservice.org.uk. for more information. The min contributions employers and their staff must pay into their workplace. The Pension scheme has increased with effect from 6 April 2019. Anyone employing staff should check that these legal obligations are being complied with.
One-person limited companies are exempt from pensions auto-enrolment. It ensures that the employer is the only employee. The organization does not have to have a workplace pension.
Working out how best to utilize pension contributions tax relief can Complicate it. To seek professional advice which recommends.
Extra note: FA 2004, Part 4