To decide your organization’s benefits or misfortunes, and to have the option to figure charges towards the finish of the monetary year, you need to record a book of passage. Accounting records all deals for an organization and fills in as the reason for the benefit and misfortune account and the readiness of the balance sheet. Along with the pay proclamation, it is a principle part of the yearly report.
What is a balance sheet, and how would you Make one?
The balance sheet is an assertion of an organization’s resources and liabilities at a given point on the schedule. It’s partitioned into two sections, with the resources on the left and the liabilities on the right. The resources site gives data on the organization’s assets. The liabilities side shows the organization’s commitments. It’s significant that the absolute amount of resources consistently coordinates with the complete liabilities.
This is then neutralized on the liabilities side, which records value, obligation capital, and cash owed to providers. The things recorded are summed up yet to be determined sheet and dispensed aside or the other. In basic terms, value capital can be determined from the balance sheet by deducting acquired capital (liabilities) from the absolute resources. So, the accompanying applies:
Assets = liabilities (capital)
Assets = equity+ liabilities
Which can be reworked into:
Equity = Assets – liabilities
Interested in ACCOTAX – Accountants in London? Why not speak to one of our qualified accountants? Give us a call on 0203 4411 258 or request a callback.
Who should Make a Balance Sheet?
The UK has no particular necessities about how you decide to keep your books, and the formation of a balance sheet can be barred relying upon the kind of business. By and large, however, balance sheets are required and should contain a specific measure of data.
The construction and size can be deftly founded on the size of the organization and the necessary intricacy. Private ventures, for instance, will in general have a lot more straightforward balance sheets than enormous partnerships. Indeed, even as a business person, however, a balance sheet and benefit and misfortune report are a smart thought to assist keep with the following of your monetary exhibition.
Unincorporated organizations in the UK are not needed to make a balance sheet, however, they might in any case decide to do as such.
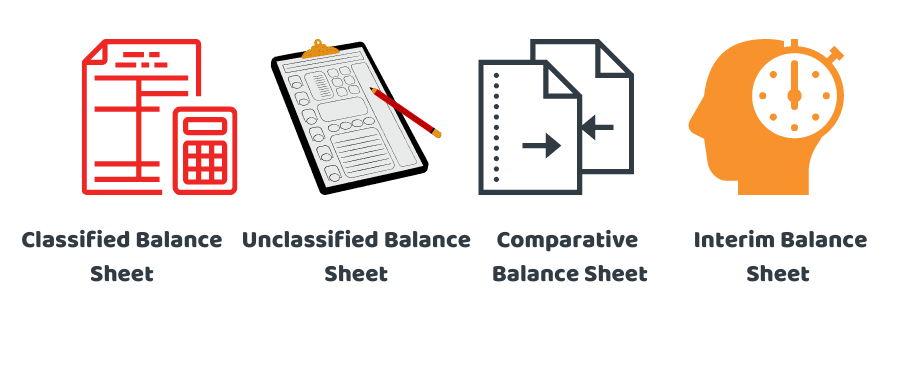
What Types of Balance Sheets are there?
There are not many essential kinds which you can make to suit various purposes. They are mentioned and explained below:
1- Classified Balance Sheet:
The most famous sort, an classified balance sheet separates data by subcategories. These classifications are then characterized to make it simple to discover the data being referred to. There are no necessities about which classifications should be incorporated, yet keeping a predictable construction improves on the most common way of looking at data over numerous periods.
2- Unclassified Balance Sheet:
This one doesn’t utilize the classifications and subcategories of the ordered variant and rather records all things immediately. Resources are by and large arranged first, trailed by liabilities. There are no subtotals as would be remembered for an ordered one, yet rather aggregates are recorded for resources, liabilities, and values. This kind of balance sheet is for the most part reasonable for little reports with not many things to list, or for inner announcing purposes.
Resources are recorded by their liquidity, with cash resources at the top and fixed resources at the base. Liabilities are additionally introduced along these lines, by and large, coordinated by the due date.
3- Comparative Balance Sheet:
A comparative balance sheet is utilized to look at account balances at various focuses on schedule. This is especially valuable for acquiring an outline of the organization’s overall monetary position, for example, the direction of its total assets and obligations. The subtotals for the different focuses in time are introduced one next to the other. Relative balance sheets are the necessary structure under FRS 102, very much like with the old UK GAAP.
4- Interim Balance Sheet:
Since balance sheets are formed to envelop a whole monetary year, the expression “between time” doesn’t actually apply to them. Notwithstanding, interval fiscal summaries can be helpful to introduce periods that cover short of what one year.
For instance, openly held organizations that are needed to give quarterly reports might utilize between time balance sheets. Since it is simply used to allude somewhat to schedule, not a range of time, the brake balance sheet will contrast marginally from different reports remembered for a between time fiscal summary.
How would you Make a Balance Sheet?
The construction ordinarily follows the characterized style. The qualities for the individual things are taken from information in the bookkeeping records that were utilized to record all deals for the monetary year. For instance, in the event that the acquisition of a machine was financed with an advance, the worth of the “property, plant, and gear” (resource side) increments – thus does the worth of the relating obligation on the opposite side.
Devaluation for mileage, for example, the decay of the machine, and the interest paid on the advance are recorded in the benefit and misfortune report to change benefit sums. The determined benefit or misfortune is displayed under the balance sheet thing “value” on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Thinking of switching ACCOTAX? See our simple guide.
Assets:
On the resources side, a qualification is made between current resources and non-current resources. The thing that matters depends on how long they’re held for. Here, fixed resources are long haul, like hardware and vehicles. These resources stay in the organization for a more drawn-out time frame. Current resources, then again, are “available for use”, for example, completed items, products, and things that the organization needs for additional preparing (material), just as receivables from clients (open solicitations), money, and bank resources.
Property, plant, and gear incorporates long-haul resources that are gained for functional use in the organization. Securing costs for these resources deteriorate as they’re utilized, contingent upon the resource and yearly mileage, on a star rata premise, which diminishes the benefit. It’s then, at that point recorded yet to be a determined sheet at the individual conveying esteem.
Liabilities:
The liabilities side shows the wellspring of the capital. It records value, arrangements, liabilities, and, if relevant, conceded pay just as conceded charge liabilities. The liabilities show where or to whom the organization owes something and what the proprietor is qualified for.
On this side, development is significant. Investors’ value is viewed as long haul capital that remaining parts of the organization for quite a while, with other long haul liabilities, for example, home loans and bank advances recorded beneath. The circumstance is diverse for transient liabilities, for example, provider solicitations – these are typically settled inside a couple of days and in this manner are situated lower than long haul liabilities.
Arrangements are liabilities whose worth is not set in stone: These incorporate expenses, annuity installments, and expected case costs from forthcoming procedures.
Conclusion:
As a rule, the making of a balance sheet and pay articulations requires a specific measure of master information. However you’re unquestionably not needed to, it’s prudent to recruit an expense advisor to set up your yearly fiscal summaries.
Still, have a question? Get in touch with us.
Disclaimer: This article intends to provide general information on the balance sheet and its types.