Many successful investors use different metrics to access the performance of a company. One of the fundamental financial and accounting metrics to determine the company’s stock value is its book value and market value. These represent the different aspects of the value of assets. In this article, we’ll be discussing book value vs market value, and we’ll break down both to understand the difference and similarities between them. Let’s dive in!
Accotax is one of the leading accounting and tax firms in the UK specialising in putting cash back into your pocket. Let us help you to claim your tax back. Give us a call on 0203 4411 258 or request a callback!
Book Value vs Market Value: A Quick Glance
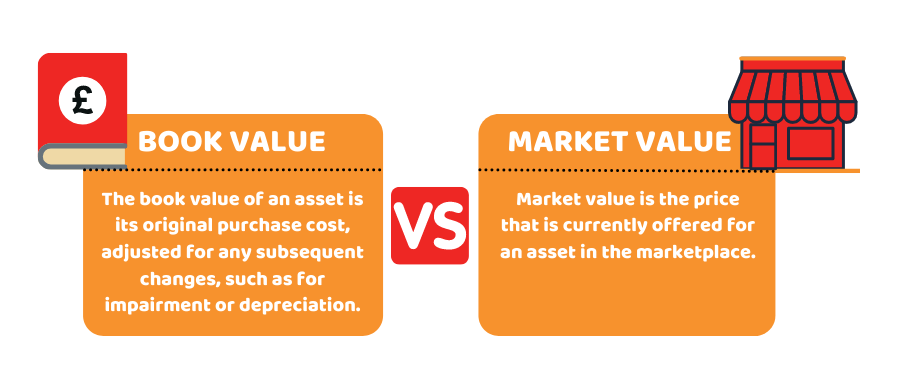
Market value is the value or amount of an asset in a marketplace. It is the price that people are currently willing to pay for the company’s stock. Whereas, the book value is the concept related to the asset’s value recognised by the company on its balance sheet. It is similar to the net asset value of a firm. Book value is the amount of money that a company would pay its shareholders when liquidated.
Book Value
As the name suggests, the book value (also known as carrying value or net asset value) means the value of the business according to its accounts or books on the balance sheet. In essence, it is the value determined as the original cost paid for acquiring assets, adjusted for any subsequent changes like depreciation, amortisation or impairment.
Theoretically, it is the amount the investors or shareholders get when they sold all company’s assets after paying off its liabilities and debts. In this way, it is the amount shareholders receive when a company goes into a liquidation.
In accounting, book value is a helpful indicator to determine the value of a company’s equity. So it is the equity value the shareholders receive at the time of company liquidation. Frequently, it is used to work out whether the value of an asset is underpaid or overpaid. It is determined by comparing the difference between the market value and book value.
Book Value Formula
Book value is the difference between the company’s total assets and the total liabilities of the company. Here is the formula:
Book value of a company=Total assets − Total liabilities
Total assets include all financial assets, physical assets and sometimes intangible assets too. Example includes cash, machinery, plants, etc. On the other hand, total liabilities include accounts payable, debt obligation, deferred taxes etc.
Looking for someone to help you with record-keeping, preparing annual accounts and overall tax liabilities, Accotax is here to help. Whether you are an LLP or a limited company, be sure to get in touch with us today for a quote!
Market Value
Market value is the current existing cost for an asset in the marketplace. It represents the value of the company as per the stock market. In other words, it is the amount received by selling the asset on a competitive, open market. The market value of publicly traded companies is dynamic and it frequently changes based on the changes in its stock price.
This value helps to determine the value of highly liquid assets like equities. On the other hand, finding the market value of assets that are not liquid is a complex process. This value is greater than the book value of the company as it captures profitability, future growth prospects and intangibles.
Market Value Formula
Market value is calculated by multiplying a company’s outstanding shares by its current market price.
Market cap of a company=Current market price (per share)∗Total number of outstanding shares
Quick Sum Up
Understanding book value vs market value is of crucial importance to work out the financial strength of the company. Investors compare the difference between the market and book value of the company to know the company’s ability to generate revenue. However, you must know that these two values are not to be all or the end of all financial metrics as there are a lot of other measures to determine the business’s value.
Still, confused? Talk to our Experts to get your queries answered swiftly!
Rely on Accotax to sort out your accounting, tax, payroll and cash flow issues. Feel free to schedule a meeting!
Disclaimer: This blog is written for general information only.